Next: 5.4 Using iteration. Up: 5 Explained exercises Previous: 5.2 A bit more Contents
This one,
![]() ,
is more interesting:
,
is more interesting:
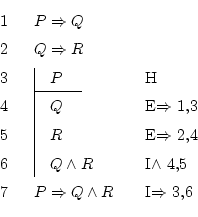
Note the following details:
It isn't hard to understand why:
![]() says that
if it happens
says that
if it happens ![]() , then happens
, then happens ![]() , so the first
we should do is to suppose that
, so the first
we should do is to suppose that ![]() really does happen. Then we will
have to discover that, in this case when
really does happen. Then we will
have to discover that, in this case when ![]() is true, it is also
true
is true, it is also
true ![]() . When we get that, we will apply the rule and write
everything politely:
. When we get that, we will apply the rule and write
everything politely:
![]() .
.
For that reason, at line 3 we make an hypothesis (justified by the
![]() at the right): suppose that
at the right): suppose that ![]() is true. Now we're starting
a subdemonstration, where we will be able to use the truths that were
on the father demonstration (lines 1 and 2 in this case), and also
we can use
is true. Now we're starting
a subdemonstration, where we will be able to use the truths that were
on the father demonstration (lines 1 and 2 in this case), and also
we can use ![]() as if it were another truth.
as if it were another truth.
We made this hypothesis aiming to know that ![]() , so we deduce
it similarly to the previous exercises. Notice that we use truths
from inside and from outside the subdemonstration, and also that,
while we haven't finished it, that vertical line to the left must
be put.
, so we deduce
it similarly to the previous exercises. Notice that we use truths
from inside and from outside the subdemonstration, and also that,
while we haven't finished it, that vertical line to the left must
be put.
In line 6 we now have ![]() , which is what we were looking
for. Using the implication introduction rule, we can go outside
this subdemonstration by saying that if the hypothesis is true,
then what we deduced from it also is true. We stop putting that vertical
line, since
, which is what we were looking
for. Using the implication introduction rule, we can go outside
this subdemonstration by saying that if the hypothesis is true,
then what we deduced from it also is true. We stop putting that vertical
line, since
![]() is always true (it doesn't depend
on whether
is always true (it doesn't depend
on whether ![]() is true or not). The justification we used,
is true or not). The justification we used,
![]() ,
says that 3 is the line where we made the supposition, and 6 the line
where we discovered something interesting which happens when we make
that supposition.
,
says that 3 is the line where we made the supposition, and 6 the line
where we discovered something interesting which happens when we make
that supposition.
![]() is what we wanted, so we have finished.
We finish as always, since we're outside any subdemonstration.
is what we wanted, so we have finished.
We finish as always, since we're outside any subdemonstration.
Daniel Clemente Laboreo 2005-05-17